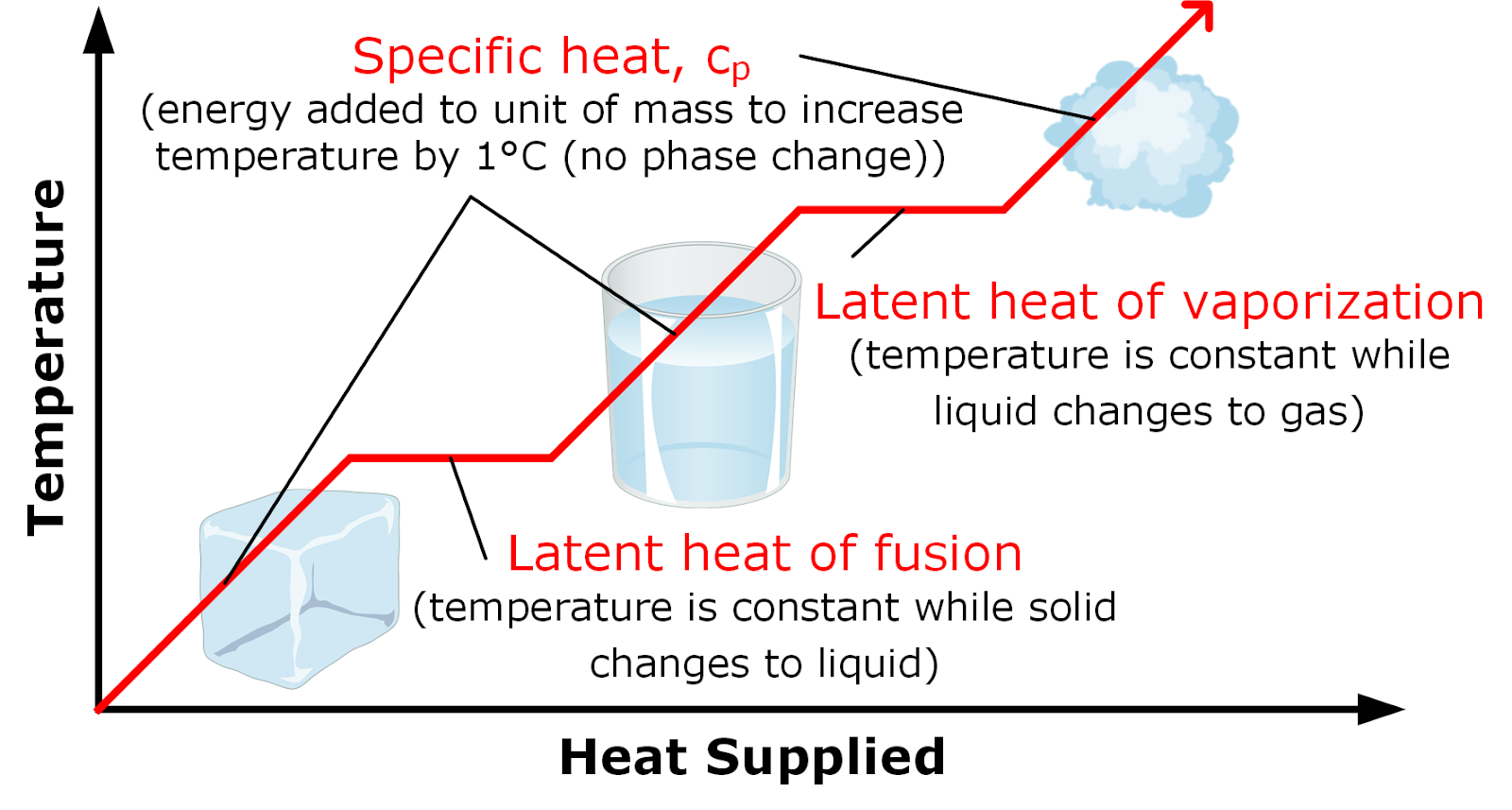
Evaporation And Specific Heat . Evaporation refers to the change of phase occurring at the air or gas interface formed with a liquid medium. The symbol c stands for the specific heat (also called “specific heat capacity”) and depends on the material and phase. The molar heat of vaporization \(\left( \delta h_\text{vap} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed by one mole of that substance as it is. The quantity of heat required to convert a liquid into vapour at a constant temperature related to a unit of mass ( 1 k g or 1 g) is called the specific. The heat (or enthalpy) of vaporization is the quantity of heat that must be absorbed if a certain quantity of liquid is vaporized at a constant temperature. The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance, to.
from guides.co
The molar heat of vaporization \(\left( \delta h_\text{vap} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed by one mole of that substance as it is. The heat (or enthalpy) of vaporization is the quantity of heat that must be absorbed if a certain quantity of liquid is vaporized at a constant temperature. Evaporation refers to the change of phase occurring at the air or gas interface formed with a liquid medium. The symbol c stands for the specific heat (also called “specific heat capacity”) and depends on the material and phase. The quantity of heat required to convert a liquid into vapour at a constant temperature related to a unit of mass ( 1 k g or 1 g) is called the specific. The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance, to.
States of Matter FD202 Fundamentals of Fire and Combustion on Guides
Evaporation And Specific Heat Evaporation refers to the change of phase occurring at the air or gas interface formed with a liquid medium. The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance, to. The quantity of heat required to convert a liquid into vapour at a constant temperature related to a unit of mass ( 1 k g or 1 g) is called the specific. The molar heat of vaporization \(\left( \delta h_\text{vap} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed by one mole of that substance as it is. Evaporation refers to the change of phase occurring at the air or gas interface formed with a liquid medium. The symbol c stands for the specific heat (also called “specific heat capacity”) and depends on the material and phase. The heat (or enthalpy) of vaporization is the quantity of heat that must be absorbed if a certain quantity of liquid is vaporized at a constant temperature.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Physics 132 Written Homework Problems Week 1 Problem Evaporation And Specific Heat The quantity of heat required to convert a liquid into vapour at a constant temperature related to a unit of mass ( 1 k g or 1 g) is called the specific. The molar heat of vaporization \(\left( \delta h_\text{vap} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed by one mole of that substance as it is. The symbol c. Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From www.saltworkconsultants.com
Physics of evaporation Evaporation And Specific Heat Evaporation refers to the change of phase occurring at the air or gas interface formed with a liquid medium. The heat (or enthalpy) of vaporization is the quantity of heat that must be absorbed if a certain quantity of liquid is vaporized at a constant temperature. The quantity of heat required to convert a liquid into vapour at a constant. Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Find the change in entropy when 87.3 g of water vapor condense Evaporation And Specific Heat The molar heat of vaporization \(\left( \delta h_\text{vap} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed by one mole of that substance as it is. The quantity of heat required to convert a liquid into vapour at a constant temperature related to a unit of mass ( 1 k g or 1 g) is called the specific. The (latent) heat. Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 25.1 “ Factors that Affect Climate ” PowerPoint Evaporation And Specific Heat The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance, to. The symbol c stands for the specific heat (also called “specific heat capacity”) and depends on the material and phase. Evaporation refers to the change of phase occurring. Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From study.com
Latent Heat Definition, Formula & Examples Video & Lesson Transcript Evaporation And Specific Heat The quantity of heat required to convert a liquid into vapour at a constant temperature related to a unit of mass ( 1 k g or 1 g) is called the specific. The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to. Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From www.teachoo.com
How does Evaporation cause cooling? Explain (with Examples) Teachoo Evaporation And Specific Heat The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance, to. The molar heat of vaporization \(\left( \delta h_\text{vap} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed by one mole of that substance as it is. The heat (or. Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From www.myxxgirl.com
Phase Change Evaporation Condensation Freezing Melting Sublimation My Evaporation And Specific Heat The symbol c stands for the specific heat (also called “specific heat capacity”) and depends on the material and phase. The heat (or enthalpy) of vaporization is the quantity of heat that must be absorbed if a certain quantity of liquid is vaporized at a constant temperature. The molar heat of vaporization \(\left( \delta h_\text{vap} \right)\) of a substance is. Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From www.tec-science.com
Specific latent heat of condensation tecscience Evaporation And Specific Heat Evaporation refers to the change of phase occurring at the air or gas interface formed with a liquid medium. The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance, to. The heat (or enthalpy) of vaporization is the quantity. Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From www.sliderbase.com
Thermodynamics Presentation Chemistry Evaporation And Specific Heat Evaporation refers to the change of phase occurring at the air or gas interface formed with a liquid medium. The quantity of heat required to convert a liquid into vapour at a constant temperature related to a unit of mass ( 1 k g or 1 g) is called the specific. The molar heat of vaporization \(\left( \delta h_\text{vap} \right)\). Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From present5.com
Thermodynamics I Te mperature Thermal Equilibrium and Evaporation And Specific Heat The heat (or enthalpy) of vaporization is the quantity of heat that must be absorbed if a certain quantity of liquid is vaporized at a constant temperature. Evaporation refers to the change of phase occurring at the air or gas interface formed with a liquid medium. The molar heat of vaporization \(\left( \delta h_\text{vap} \right)\) of a substance is the. Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From www.youtube.com
Change in ENTHALPY Using Specific Heat at Constant Pressure in 3 Evaporation And Specific Heat The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance, to. The quantity of heat required to convert a liquid into vapour at a constant temperature related to a unit of mass ( 1 k g or 1 g). Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From www.tec-science.com
Specific latent heat of vaporization tecscience Evaporation And Specific Heat The symbol c stands for the specific heat (also called “specific heat capacity”) and depends on the material and phase. The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance, to. Evaporation refers to the change of phase occurring. Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From www.chegg.com
Solved 7. Evaporation is to be used to concentrate 3000 kg/h Evaporation And Specific Heat The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance, to. The quantity of heat required to convert a liquid into vapour at a constant temperature related to a unit of mass ( 1 k g or 1 g). Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From jramnax.blogspot.com
Specific Latent Heat Of Evaporation Formula Specific Heat Capacity Evaporation And Specific Heat The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance, to. The quantity of heat required to convert a liquid into vapour at a constant temperature related to a unit of mass ( 1 k g or 1 g). Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From www.solutionspile.com
[Solved] Problem 1 Specific heat and evaporation The spec Evaporation And Specific Heat Evaporation refers to the change of phase occurring at the air or gas interface formed with a liquid medium. The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance, to. The heat (or enthalpy) of vaporization is the quantity. Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From brainly.in
how does evaporation cause cooling?? Brainly.in Evaporation And Specific Heat The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance, to. Evaporation refers to the change of phase occurring at the air or gas interface formed with a liquid medium. The molar heat of vaporization \(\left( \delta h_\text{vap} \right)\). Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From guides.co
States of Matter FD202 Fundamentals of Fire and Combustion on Guides Evaporation And Specific Heat The (latent) heat of vaporization (∆h vap ) also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance, to. Evaporation refers to the change of phase occurring at the air or gas interface formed with a liquid medium. The molar heat of vaporization \(\left( \delta h_\text{vap} \right)\). Evaporation And Specific Heat.
From www.researchgate.net
Specific Heat Capacity (C p ) and Thermal Conductivity (k) with Density Evaporation And Specific Heat The molar heat of vaporization \(\left( \delta h_\text{vap} \right)\) of a substance is the heat absorbed by one mole of that substance as it is. The quantity of heat required to convert a liquid into vapour at a constant temperature related to a unit of mass ( 1 k g or 1 g) is called the specific. Evaporation refers to. Evaporation And Specific Heat.